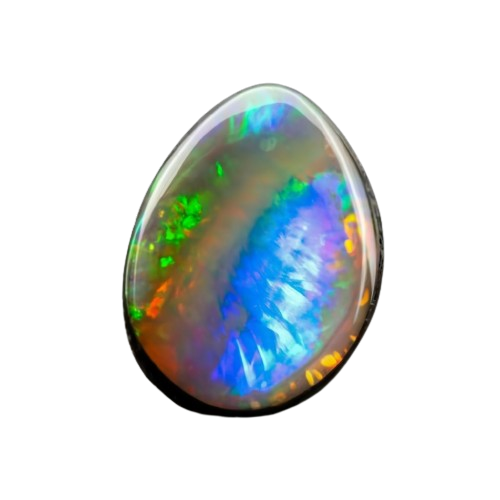
[Black Opal]: Discover the Magic, Beauty and Brilliance
What Are Opals?
Black Opal is an amorphous silica (SiO2·nH2O) with a water content that can range from 3 to 21% by weight, although it usually falls between 6 and 10%. It is distinguished from crystalline forms of silica that are regarded as minerals by its non-crystalline structure, which is what makes it a mineraloid. Deposited at low temperatures, opal can be found in the clefts of a variety of rocks; it is frequently found with limonite, sandstone, rhyolite, marl, and basalt.
- Origin of the Term “Opal”:
- Thought to originate from the Sanskrit word “upala” (उपल), meaning ‘jewel’.
- Derived into the Greek term “opállios” (ὀπάλλιος).
- Composition of Opals:
- Mainly comprised of silica SiO2.
- Contains water content of up to 20%, typically ranging from 4-10%.
- Lack a crystalline structure and do not possess directional optical properties.
- Formation Process:
- Opals form as hot, silica-rich solutions permeate through veins and voids in the earth’s surface.
- Commonly found in volcanic or sedimentary settings.
- The solution precipitates at lower temperatures over extended periods, leading to the gradual accumulation of layers of minute silica spheres.
- Optical Phenomena and Coloration:
- Opals consist of regularly stacked, three-dimensional groups of spheres of equal size.
- Optical phenomena occur due to the interaction of light with these silica spheres.
- When viewed from various angles in the light, opals exhibit patches of spectral color, resulting in their characteristic iridescence.
Categories:
- Two Primary Categories of Opal:
- Precious Opal: Exhibits play-of-color, characterized by iridescence.
- Common Opal: Lacks play-of-color and iridescence.
- Play-of-Color:
- Refers to a pseudo chromatic optical effect where certain minerals emit flashes of colored light when viewed under white light.
- Caused by the internal structure of precious opal, which leads to light diffraction.
- Transparency Variation:
- Opal can vary in transparency, ranging from transparent to translucent to opaque.
- Transparency affects the visibility of the internal play-of-color phenomenon.
- Background Color Variation:
- Opals may exhibit a background color of white, black, or nearly any hue across the visual spectrum.
- The background color influences the overall appearance and aesthetic appeal of the opal.
- Rareness of Black Opal:
- Black opal is considered the rarest among opals due to its distinct and intense play-of-color against a dark background.
- White, gray, and green opals are more prevalent in comparison.
Precious opal:
Despite being categorized as a mineraloid with an internal structure, precious opal exhibits a dynamic interplay of internal colors.
Microscopic Structure of Precious Opal:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica spheres |
| Diameter of Silica Spheres | Approximately 150–300 nm (5.9×10−6–1.18×10−5 in) |
| Arrangement of Spheres | Hexagonal or cubic close-packed lattice |
Light Interaction Mechanism:
| Light Interaction Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Researcher | J. V. Sanders |
| Time Period | Mid-1960s |
| Mechanism | Orderly silica spheres generate internal colors through interference and diffraction of light |
| Influence Factors | Uniformity of sphere sizes and their arrangement |
| Diffraction Phenomenon | When spacing between stacked planes of spheres is ~half the wavelength of visible light, diffraction occurs. Observed colors depend on spacing between planes and alignment relative to incident light. |
| Bragg’s Law of Diffraction | Describes conditions for constructive interference of light waves scattered by crystal lattice. Applies to explaining observed colors in precious opal. |
What makes an opal precious?
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Precious Opal | Opals are considered precious when they exhibit flashes of vibrant rainbow colors, known as ‘play-of-color’. |
| Play-of-Color | Unique to opal, this optical phenomenon manifests as vibrant flashes of spectral colors ranging from red to violet. |
| Spectral Colors | The best precious opals display all spectral colors from red to violet. |
| Historical Significance | Opals have been revered since antiquity for their beauty and mystery. Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder described precious opals as possessing the combined qualities of fire (ruby), brilliant purple (amethyst), and sea-green (emerald), making them highly esteemed. Opals were often regarded as the “queens of gemstones” due to their fiery and iridescent qualities, inspiring poets like William Shakespeare. |
Common opal:
In addition to the gemstone varieties that exhibit play of color, common opal encompasses several other types.
- Types of Common Opal:
- Milk Opal: Displays a milky bluish to greenish hue, sometimes of gemstone quality.
- Resin Opal: Characterized by a honey-yellow color with a resinous luster.
- Wood Opal: Resulting from the replacement of organic material in wood with opal.
- Menilite: Typically brown or grey in color.
- Hyalite: A colorless, glass-clear opal also known as Muller’s glass.
- Geyserite: Also known as siliceous sinter, formed around hot springs or geysers.
- Diatomaceous Earth: Composed of accumulations of diatom shells or tests.
- Opalescence in Common Opal:
- Common opal often exhibits a hazy-milky-turbid sheen from within the stone.
- In gemology, this optical effect is specifically termed opalescence and is a form of adularescence.
What Are Black Opals?
The tiny particles in this opal’s composition are responsible for its deep color. These trace elements can have different kinds. The dark color is mostly attributed to iron and carbon sulfides (pyrite and chalcopyrite), which are produced microbiologically during the solidification process. Depending on the conditions under which they formed, these opals’ dark body color can range from pure black to dark grey or chocolate brown.
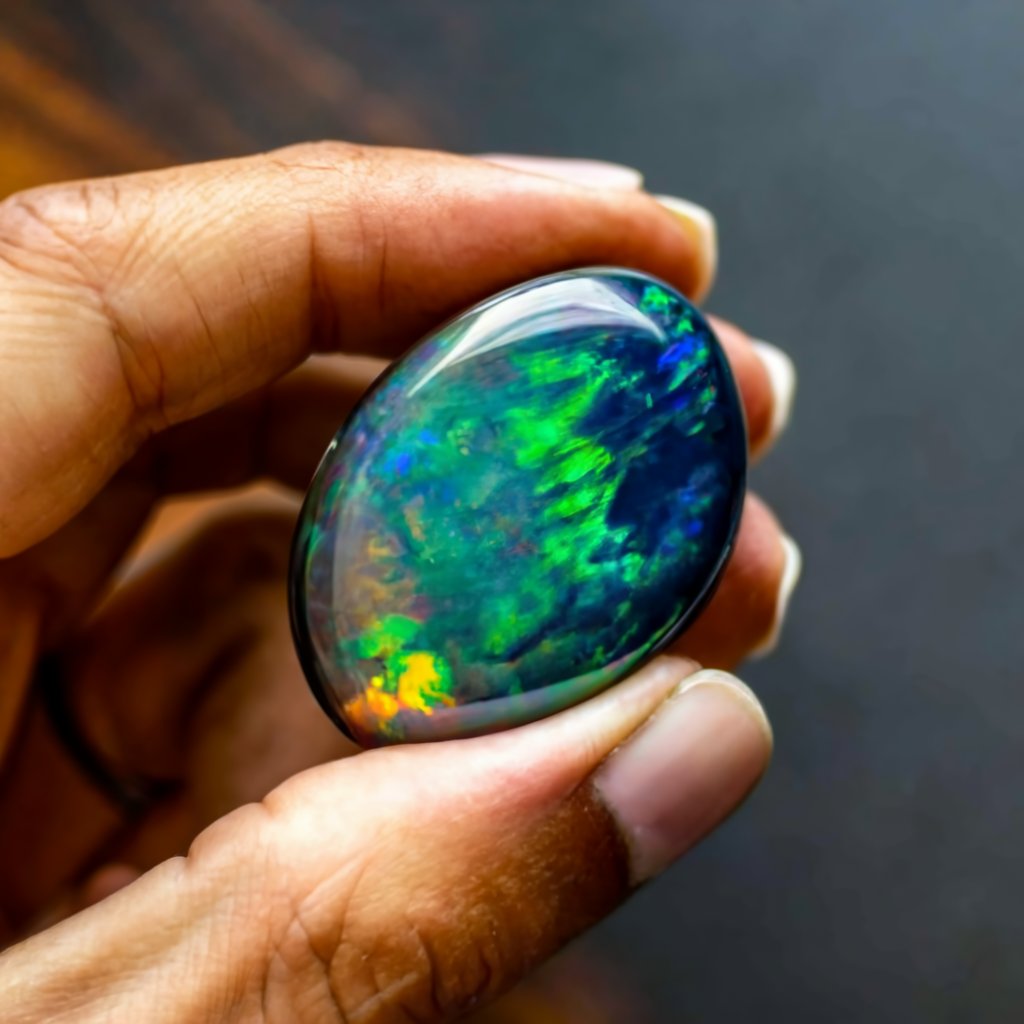

- Black Stone Opal Characteristics:
- This Opal is a highly valued gemstone known for its captivating play-of-color.
- It belongs to the category of precious opals.
- The gem displays a dark or black body color.
- It features vibrant flashes of iridescent colors that seem to move and change when viewed from different angles.
- Play-of-Color:
- The play-of-color in this Opal includes hues such as blue, green, red, orange, and purple.
- This mesmerizing display of colors makes this Opal one of the most sought-after opals globally.
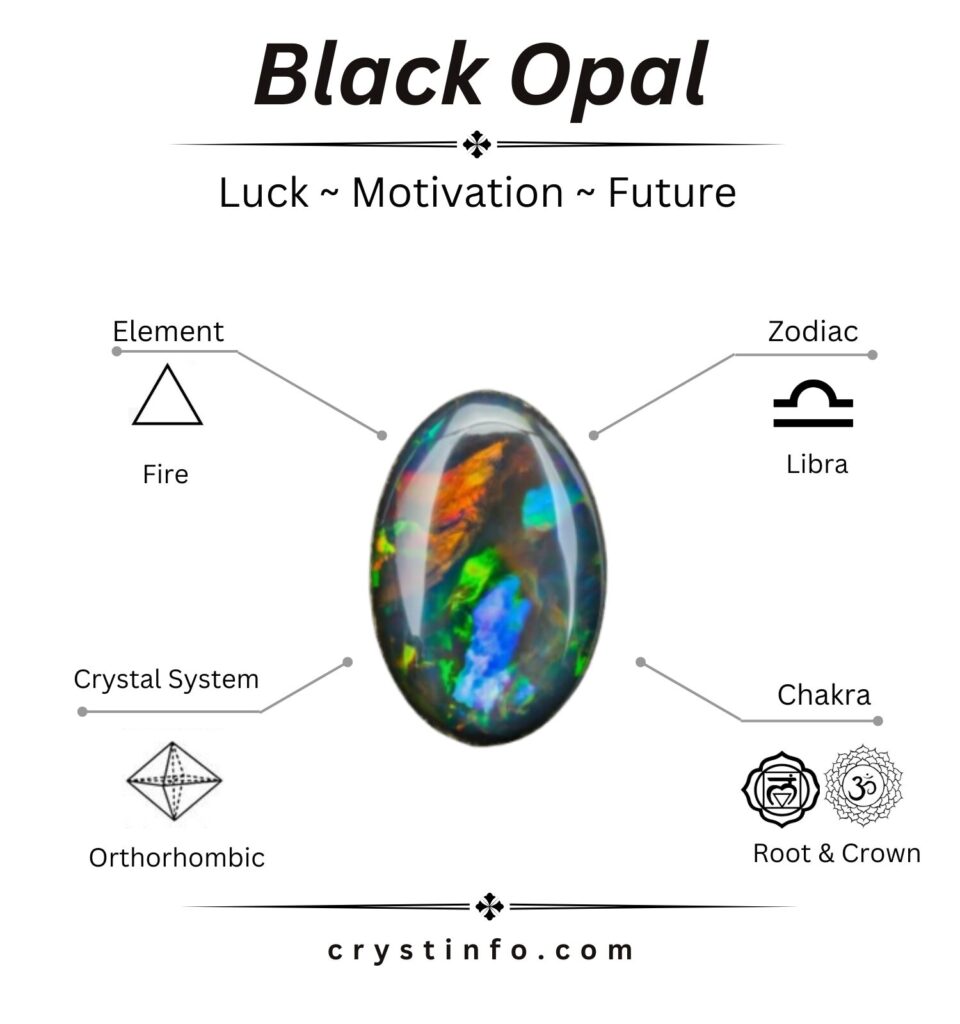
Characteristics:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Black Opal |
| Composition | A form of opal with a dark body color, often displaying vibrant play-of-color in various hues. |
| Color | Predominantly black or dark gray body color with flashes of vibrant colors, including blues, greens, and reds. |
| Luster | Vitreous to resinous |
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque |
| Hardness | 5.5 – 6.5 on the Mohs scale |
| Crystal System | Amorphous |
| Fracture | Conchoidal to uneven |
| Cleavage | None |
| Specific Gravity | 1.98 – 2.20 |
| Streak | White to colorless |
| Occurrence | Found in Australia, particularly in Lightning Ridge, New South Wales, which is famous for its black opals. |
| Uses | – Gemstone Use: Highly valued as a gemstone for jewelry due to its striking play-of-color and rarity. |
| – Ornamental Use: Often used in decorative items and ornamental pieces. | |
| Play-of-Color | This opals are prized for their vibrant play-of-color, which is caused by the diffraction of light through tiny silica spheres in the stone. |
| Value | This opals are considered one of the rarest and most valuable forms of opal, with prices determined by the intensity and distribution of their play-of-color. |
| Care | This opals should be handled with care to avoid scratching or chipping, and exposure to harsh chemicals should be avoided. Cleaning with mild soap and water is recommended. |
This opal is renowned for its captivating play-of-color against a dark background, making it highly sought after in the world of gemstones and jewelry.
Hardness:
Gravity:
Types and Varieties:
There are several varieties of opals, and each is distinguished by special qualities and appearances. One variety of opal that is highly prized for its vivid play of color and dark body color is opal. The various opal varieties and how this Opal fits into them are as follows:
| Opal Variety | Description |
|---|---|
| White Opal | Most common type of opal with a light to white body color. Play-of-color is subdued compared to this Opal. Generally considered less valuable than more vividly colored opals. |
| Black Opal | Features a dark to black body color with enhanced play-of-color, displaying striking flashes of vibrant hues. Among the most prized and valuable opals due to captivating beauty. |
| Boulder Opal | Unique type of opal forming within ironstone or sandstone boulders. Opal fills cavities and cracks in the host rock. It has a dark body color similar to this Opals and can display remarkable play-of-color. |
| Crystal Opal | Characterized by a transparent to translucent appearance with highly visible play-of-color. Body color varies from clear to pale and dark tones. Often exhibits intense and vibrant play-of-color, making it highly desirable. |
| Fire Opal | Distinct from other opals with fiery orange, red, or yellow body color, displaying a uniform hue throughout the gemstone. Not as highly valued as opals with play-of-color but prized for their rich color. |
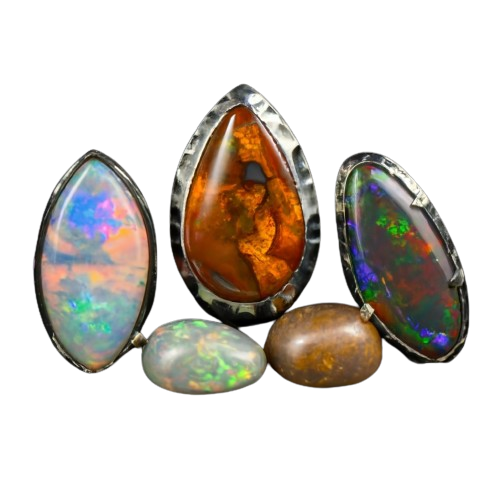

Every Opal variety has a unique and captivating beauty that attracts collectors and gemstone enthusiasts from all over the world.
Famous Opals:
'Burning of Troy' Opal:
| 'Burning of Troy' Opal | Description |
|---|---|
| Naming | Named for the blazing red flashes burning within the black gem. |
| Historical Gift | Gifted by Emperor Napoleon to his wife Joséphine, known as his beloved 'Helen'. |
| Weight | Weighed 700 carats and regarded as the most beautiful and valuable black opal. |
| Origin | Believed to have been mined in Honduras. |
| Status | Lost to history, adding to its mystique and allure. |
'Aurora Australis' Opal:
| 'Aurora Australis' Opal | Description |
|---|---|
| Discovery | Found in Lightning Ridge, considered the world's most valuable this opal. |
| Year of Discovery | Discovered in 1938 and polished into an oval shape, weighing 180 carats. |
| Play-of-Color | Displays a vibrant play-of-color with dominant hues of red, green, and blue against a black background. |
| Geological Origin | Dug from an old sea-bed, featuring a distinctive impression of a starfish on its back. |
| Valuation | Valued at AUD$1 million in 2005, highlighting its rarity and beauty. |
Grading and Evaluation:
Experts and gemologists assess a number of factors that determine the quality and value of black gem. These elements are essential in determining the gemstone's overall desirability and market value. The following are the main variables influencing this opal prices:
- Play-of-Color:
- Most important factor influencing this Opal's value.
- Bright, vivid colors and large areas of play-of-color increase value.
- Intensity, vibrancy, and distribution of colors across the gemstone impact appeal.
- Body Color:
- Darkness and tone of opal’s body color are significant.
- Deep and dark body colors provide better contrast to play-of-color.
- Enhances overall visual impact of the gem.
- Transparency:
- Higher transparency allows more light to pass through.
- Opals with higher transparency are generally more prized.
- Pattern:
- Pattern of play-of-color is crucial.
- Opals with rare and unique patterns, like harlequin, are highly sought after.
- Command higher prices due to rarity and visual appeal.
- Brilliance:
- Brightness and vibrancy of play-of-color are essential.
- Opals displaying vibrant and sharp flashes of color are more valuable.
- Size and Shape:
- Larger Opals are rarer and more valuable.
- Certain shapes, such as oval or cushion, maximize display of play-of-color.
- Enhances gem’s attractiveness and value.
- Origin:
- Locality of mining influences opal's value.
- Opals from well-known sources like Lightning Ridge are more prized.
- History of producing high-quality gems adds to their value and desirability.
Jewelry:
This opal's captivating color play and striking appearance make it a highly sought-after and prized gemstone for jewelry. It gives any piece of jewelry a dash of uniqueness and brilliance. The following are some typical jewelry applications for this opal:
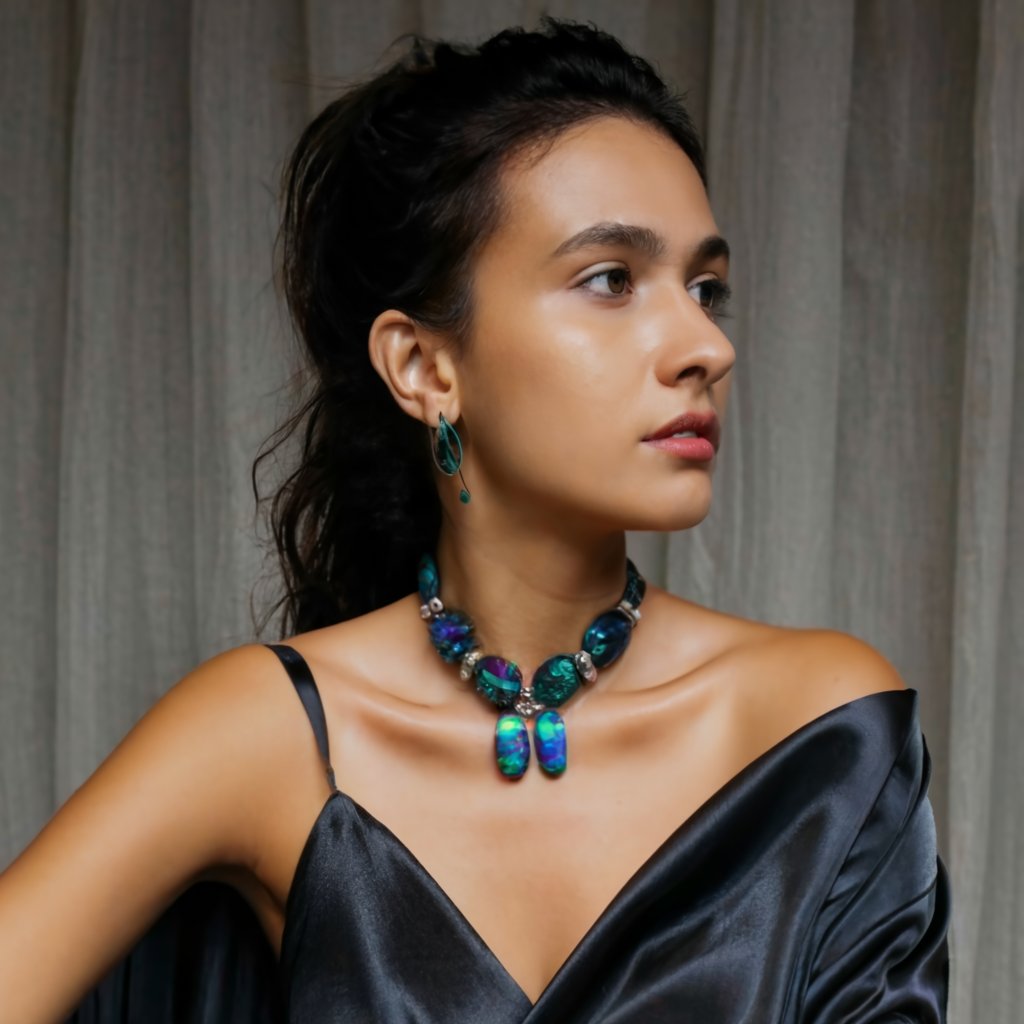

| Jewelry Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Rings | This Opal often serves as the centerpiece in statement or cocktail rings due to its dark body color and vibrant play-of-color, making it a stunning focal point for eye-catching designs. |
| Pendants and Necklaces | This Opals are frequently used in pendants and necklaces, where they can dangle freely or be surrounded by accent stones like diamonds or other colored gemstones, highlighting the opal’s beauty and prominently displaying the play-of-color. |
| Earrings | This Opals can be set as studs or dangle earrings, providing an elegant and sophisticated look. Earrings can be designed to showcase the opal’s play-of-color when they catch the light. |
| Bracelets | This Opals can be incorporated into bracelet designs, adding a touch of opalescence and color to the wrist. |
| Brooches and Pins | This Opals are used in brooches and pins to create unique and artistic designs, combining the opal’s play-of-color with intricate metalwork, resulting in real works of art. |
| Opal Doublets and Triplets | To enhance durability and appearance, some jewelry pieces feature opal doublets or triplets, composed of thin layers of opal combined with other materials like this onyx or clear quartz. This technique offers more affordable and sturdy opal jewelry. |
| Opal Inlays | This Opals are sometimes used as inlays in rings or bracelets, where the opal is cut and set into a groove or depression in the metal, creating a seamless and stunning display of color. |
Opal treatments:
Sugar and Sulfuric Acid Treatment:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Sugar and Sulfuric Acid | Opals are soaked in a sugar solution for a few days and then in sulfuric acid. The acid turns the sugar into carbon, leaving minute particles of black carbon in the opal, effectively darkening its body color. |
| Detection Methods | - Observation with a 10x loupe and microscope reveals black speckles, limited to a thin layer at the surface. - A pale matrix can be seen in between the black specks. - Play-of-color may appear very close to the surface. - Transmitted light through the opal and immersion in water can aid in spotting the added black particles. |
Smoking Treatment:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Smoking Treatment | Pale opals are smoked to achieve a black appearance. The opal is wrapped in paper and heated until the paper smoulders, releasing fine smoke particles. These particles enter the porous material of the opal, darkening its color. |
| Detection Methods | - Dark coloration tends to concentrate in crazed areas (surface-reaching fractures). - Black speckles may be visible with a loupe or microscope. - The source of the dark coloration can be checked with transmitted light or in immersion. |
Synthetics and Imitations:
It can be difficult to tell the difference between real and fake black opals, but there are some traits and examinations that can assist. Here are some techniques for telling real Opals apart from fakes made in a lab:
| Inspection Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Look for unique and vibrant play-of-color patterns. Natural Opals exhibit sharp and intense flashes of color against the dark body color. |
| Magnification | Examine under a jeweler’s loupe or microscope. Natural Opals reveal intricate patterns of play-of-color. |
| Body Color | Natural Opals have deep and dark body color. Lab-created opals may have a more uniform and artificial appearance. |
| Inclusions | Natural opals often contain internal inclusions and impurities. Synthetic opals typically lack these characteristics, but some lab-created opals may have inclusions. |
| Spectroscope | Identify natural opals based on characteristic absorption and emission spectra. Synthetic opals may display different spectra due to the manufacturing process. |
| Polarizing Filters | Natural opals may show a “rotating” play-of-color effect when viewed through polarizing filters, not typically seen in synthetic or imitation opals. |
| Water Absorption Test | Natural opals are porous and absorb water. A drop of water on the surface can indicate absorption or droplet formation. However, this test is not entirely conclusive as some lab-created opals can also be made porous. |
| X-ray Diffraction (XRD) | Determines crystal structure and composition, helping to differentiate between natural and synthetic opals. |
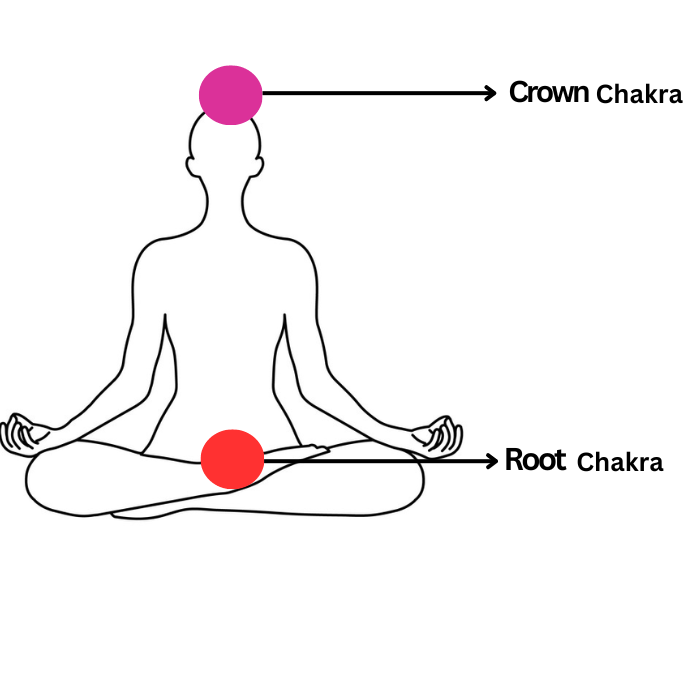
Chakra Connection:
| Chakra | Description |
|---|---|
| Crown Chakra | Also known as the seventh or Sahasrara in Sanskrit, the crown chakra is associated with spiritual connection and inner wisdom. It represents the center of our being, where we find our relationship to the universe, enlightenment, and compassion. |
| Root Chakra | This Opal is specifically linked to the root chakra, which is associated with grounding and stability. It helps strengthen the connection with the earth and promotes feelings of being grounded, especially in situations where balance is needed. |
Birthstone:
| Association | Description |
|---|---|
| Birthstone | This Opal is an October birthstone, making it a symbolic gemstone for individuals born in October. |
| Zodiac Association | This Opal is associated with the zodiac sign Libra, suggesting that it's a suitable choice for those born under the Libra sign, reflecting the qualities attributed to this astrological sign. |
Price:
- Most Expensive Opal:
- Fine quality with exquisite play of color.
- Can fetch as much as $10,000 per carat.
- Surpasses the value of an equivalent weight in diamonds.
- Dark Blue Opals from Lightning Ridge, Australia:
- Among the best varieties of this opals.
- Mined in Lightning Ridge, Australia.
- Known for their exceptional quality and play of color.
- Affordable Black Opals (Per Carat):
- Available at varying price points.
- While not as striking as the finest this opals, they can still be stunning.
- Prices range from $50 to $4,000 per carat, making them accessible to a broader range of buyers.
Side Effects:
| Concern | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Superiority Complex | Mindfully use Black Opal, focusing on humility and gratitude, to avoid feelings of superiority that excessive use may lead to. |
| Obsession | Set clear usage boundaries for Black Opal and incorporate other crystals into your practice to prevent an unhealthy obsession. |
| Disturbed Sleep | Place Black Opal away from your bed to prevent excessive energy absorption that may disrupt sleep patterns. Alternatively, use grounding stones like Hematite to mitigate its effects. |
Origin:
| Origin | Description |
|---|---|
| Lightning Ridge, Australia | Lightning Ridge, New South Wales, Australia, is renowned for producing some of the finest this opals. These opals are characterized by their dark body tone with vibrant flashes of color. |
| Mintabie, Australia | Mintabie, another locality in South Australia, has also been known to produce black opals, although the quantity and quality may vary compared to Lightning Ridge. |
| White Cliffs, Australia | White Cliffs, New South Wales, Australia, is another historic opal mining locality known for producing this opals, albeit in smaller quantities compared to Lightning Ridge. |
How to Care?
- Avoid Hard Contact:
- Opals rank about 6 on the Mohs’ scale, making them relatively soft.
- Prefer wearing opals in earrings, pendants, or brooches to prevent scratching and abrasion, rather than in rings.
- Sensitive to Humidity and Temperature:
- Opals contain water and are sensitive to variations in humidity and temperature.
- Sudden changes can cause irreversible crazing.
- Avoid displaying opals in direct sunlight.
- Storage:
- When storing opals for extended periods, place a slightly moist cotton next to them to maintain constant humidity.
- Doublets and triplets should never be soaked.
- Cleaning:
- Opals are porous to some degree, with some being absorbent, notably hydrophane opals.
- Clean opals only with a soft dry or damp cloth.
- Avoid using chemicals for cleaning.
- Refrain from testing opals on refractometers as the RI fluid might stain them.
Conclusion:
This opal, with its mesmerizing varieties like Lightning Ridge, Ethiopian, and Indonesian, mesmerizes with its depths and colors. Beyond adornment, it symbolizes transformation and protection, resonating through history and modern design. This opal embodies nature's artistry and humanity's appreciation for beauty, making it a timeless symbol of elegance and wonder.
FAQs:
- What is black opal?
- This opal is a type of precious gemstone characterized by its dark body tone and vibrant flashes of color, known as play-of-color.
- Where is this opal found?
- The most famous source of this opal is Lightning Ridge in New South Wales, Australia. Other sources include Ethiopia and Indonesia.
- What types of this opal exist?
- Black opal comes in various types, including Lightning Ridge black opal, Ethiopian black opal, and Indonesian black opal, each with its unique characteristics.
- What are the uses of this opal?
- This opal is primarily used in jewelry, including rings, necklaces, and earrings. It is also valued for its metaphysical properties and is believed to promote emotional healing and protection.
- What symbolism does this opal hold?
- This opal symbolizes transformation, protection, and emotional healing across different cultures and traditions. It is often associated with bringing luck and positive energy to its wearer.
- How do you care for this opal jewelry?
- To maintain the beauty of this opal jewelry, it is essential to avoid exposing it to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures. Cleaning with a soft cloth and mild soap is recommended, and storing it separately from other jewelry can prevent scratching.
- Is this opal rare?
- Yes, this opal is considered rare, especially high-quality specimens with intense play-of-color. Its scarcity contributes to its value and desirability in the world of gemstones.


![Strawberry Quartz: Healing Secrets and Spiritual Significance [Guide]](https://crystinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Blue-Goldstone-7-768x402.jpg)

![Opalite Gemstone: Unveiling Properties, Meanings, and [Hidden Insights]](https://crystinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Chakras-2-768x402.jpg)

![Pink Crystal:Discover Healing Wonders,[45]Types and Benefits](https://crystinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Add-a-heading-20-768x402.jpg)
![Unveiling the Power of [Red Tiger Eye]](https://crystinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Chakras-11-768x402.jpg)